물 분해
물 분할 기술은 화학 반응을 사용하여 물(H2O)을 산소와 수소로 분리하는 과정을 특징으로 합니다. 효과적인 물 분할은 전해질, 광합성, 광전기화학, 광촉매, 방사성 용해, 광생물학 및 열분해를 비롯한 다양한 기법을 사용하여 수행할 수 있습니다. 최근의 성과가 낮은 반응 온도에서 물 분할을 위한 나노입자 및 박막 촉매의 사용에 중점을 둔 바 고도의 컨퍼멀 원자층 증착(ALD: Atomic Layer Deposition)은 셀 효율을 최적화하는 데 매우 중요한 것으로 입증되었습니다. 경제적이고 효율적인 물 분할은 대체 에너지원으로서 수소 생성을 위한 중요한 요소입니다. 이 분야의 연구는 수소 경제로의 전환 가능성을 조사하고 테스트합니다.
물의 광산화
원자층 증착(ALD: Atomic Layer Deposition) 기술을 사용하여 웨이퍼 분할 응용 작업을 위한 높은 표면적 구조를 생성할 수 있습니다. 물 광산화(물 분할)를 위해 고표면적 전도 및 투명 프레임워크의 제조가 개발되었습니다.
Savannah® S200을 사용하는 원자층 증착(ALD: Atomic Layer Deposition) 필름을 역 오팔 구조물에서 ITO(in.Tin. Oxide) 및 Fe2O3에 대한 노출 모드 기술을 사용하여 증착하여, 높은 표면적 나노구조를 생성하였습니다.
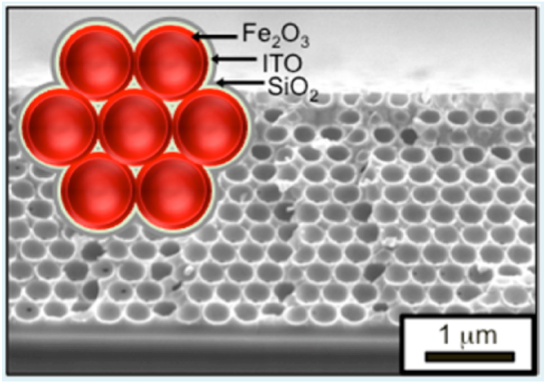
물의 광산화를 위한 높은 특정 표면적 투명 및 전도 프레임워크. 산화철 Fe2O3, ITO(in.Tin. Oxide) 및 SiO2는 역 스캐폴드 구조에서 원자층 증착(ALD: Atomic Layer Deposition)에 의해 증착됩니다. 참조: Riha, S. C, 외. Acs Appl Mater Inter 5, 360–367 (2013).
필름
- InCp, TDMASn 및 O3를 이용한 ITO(in.Tin. Oxide)
- 페로센(Fe2O3), FeCp2 및 O3 사용
결과
- 원자층 증착(ALD: Atomic Layer Deposition) 기술을 이용한 물 분할을 위해 고도로 투명하고 큰 표면적의 나노라미네이트 스택이 생성되었습니다.
- 물 산화의 시작은 -200 mV 및 1.53 V의 광전류에 의해 시프트된 반면에 가역 수소 전극은 3배가 되었습니다(일정한 광-애노드와 비교했을 때).
Fe2O3에서 Ti 치환을 통한 그린라이트 물 산화
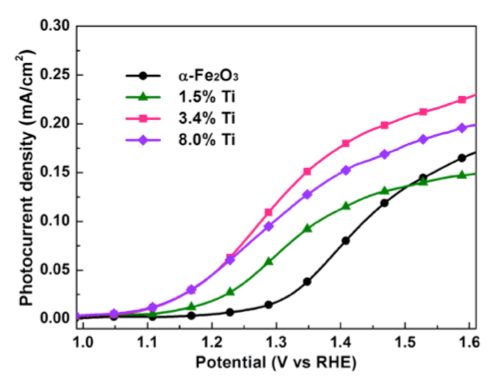
Ti 합금은 초박(6nm 두께) 적철석 변환 효율, 특히 녹색 광자에 의해 생성된 홀 수집 효율(500 – 600nm)을 개선하기 위해 사용되었습니다. Savannah® S200은 이 연구에서 TiO2 및 Fe2O3의 막을 증착하는 데 사용되었습니다.
Fe2O3의 티타늄 합금은 물의 광전기화학적 산화에 대한 촉매 활용도를 개선하기 위해 사용됩니다. 참조: Kim, D. W. et al. Greenlighting Photoelectrochemical Oxidation of Water by Iron Oxide. ACS Nano 141203161851003 (2014).
결과
- 초박 Fe2O3의 Ti 치환은 표면-국소 홀의 수명을 증가시킵니다.
- Ti-치환된 필름에서 향상된 광전류 성능이 관찰되었습니다.
- 특히 500 – 600 nm 범위에서 흡수된 광자대 전류 효율(APCE)의 개선이 관찰되었습니다.
- 광흡수에서 변화는 관찰되지 않았습니다.
참고 자료 – Veeco CNT ALD 플랫폼에서 최근 발표된 연구 결과
- Dias, P. et al. Transparent Cuprous Oxide Photocathode Enabling a Stacked Tandem Cell for Unbiased Water Splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. n/a–n/a (2015). doi:10.1002/aenm.201501537
- Luo, J. et al. Targeting Ideal Dual‐Absorber Tandem Water Splitting Using Perovskite Photovoltaics and CuInxGa1‐xSe2 Photocathodes. Adv. Energy Mater. (2015). doi:10.1002/aenm.201501520
- Landsmann, S. et al. Design Guidelines for High-Performance Particle-Based Photoanodes for Water Splitting: Lanthanum Titanium Oxynitride as a Model. ChemSusChem n/a–n/a(2015). doi:10.1002/cssc.201500830
- Barreca, D. et al. Fe2O3–TiO2 Nano‐heterostructure Photoanodes for Highly Efficient Solar Water Oxidation. Advanced Materials Interfaces n/a–n/a (2015). doi:10.1002/admi.201500313
- Michaux, K. E. et al. Visible Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Based on a Ru(II) Polypyridyl Chromophore and Iridium Oxide Nanoparticle Catalyst. The Journal of … (2015). doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b05711
- Luo, J. et al. Solution Transformation of Cu2O into CuInS2 for Solar Water Splitting. Nano Lett 15, 1395–1402 (2015).
- Schoen, D. T., Atre, A. C., García-Etxarri, A., Dionne, J. A. & Brongersma, M. L. Probing Complex Reflection Coefficients in One-Dimensional Surface Plasmon Polariton Waveguides and Cavities Using STEM EELS. Nano Lett 15, 1–8 (2014).
- Kim, D. W. et al. Greenlighting Photoelectrochemical Oxidation of Water by Iron Oxide. ACS Nano 141203161851003 (2014). doi:10.1021/nn503869n
- Azevedo, J. et al. On the stability enhancement of cuprous oxide water splitting photocathodes by low temperature steam annealing. Energy Environ. Sci. 7,4044–4052 (2014).
- Yang, X. et al. Improving Hematite-based Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting with Ultrathin TiO 2by Atomic Layer Deposition. Acs Appl Mater Inter 140804065734002 (2014). doi:10.1021/am500948t
- Klahr, B. & Hamann, T. Water Oxidation on Hematite Photoelectrodes: Insight into the Nature of Surface States through In Situ Spectroelectrochemistry. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 10393–10399 (2014).
- Zandi, O., Beardslee, J. A. & Hamann, T. Substrate Dependent Water Splitting with Ultrathin α-Fe 2O 3Electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. C 140501145249004 (2014). doi:10.1021/jp4116657
- Tilley, D. S. & Grätzel, M. Ruthenium Oxide Hydrogen Evolution Catalysis on Composite Cuprous Oxide Water-Splitting Photocathodes. Advanced Functional … 1–9 (2014). doi:10.1002/adfm201301106
- Yang, X., Du, C., Liu, R., Xie, J. & Wang, D. Balancing photovoltage generation and charge-transfer enhancement for catalyst-decorated photoelectrochemical water splitting: A case study of the hematite/MnOx combination. Journal of Catalysis 304, 86–91 (2013).
- Liu, M., Nam, C.-Y., Black, C. T., Kamcev, J. & Zhang, L. Enhancing Water Splitting Activity and Chemical Stability of Zinc Oxide Nanowire Photoanodes with Ultrathin Titania Shells. J. Phys. Chem. C 130610143036005 (2013). doi:10.1021/jp404032p
- Riha, S. C. et al. Atomic Layer Deposition of a Sub-Monolayer Catalyst for the Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Performance of Water Oxidation with Hematite. ACS Nano 130212010712000 (2013). doi:10.1021/nn305639z
- Riha, S. C., DeVries Vermeer, M. J., Pellin, M. J., Hupp, J. T. & Martinson, A. B. F. Hematite-based Photo-oxidation of Water Using Transparent Distributed Current Collectors. Acs Appl Mater Inter 5, 360–367 (2013).
- Klug, J. A. et al. Low temperature atomic layer deposition of highly photoactive hematite using iron(iii) chloride and water. J. Mater. Chem. A 1,11607 (2013).
- Maijenburg, A. W. et al. Electrochemical synthesis of coaxial TiO2-Ag nanowires and their application in photocatalytic water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A(2013). doi:10.1039/c3ta14551d
- Klahr, B., Gimenez, S., Fabregat-Santiago, F., Bisquert, J. & Hamann, T. W. Photoelectrochemical and Impedance Spectroscopic Investigation of Water Oxidation with ‘Co–Pi’-Coated Hematite Electrodes. J Am Chem Soc 134,16693–16700 (2012).
- Paracchino, A. et al. Ultrathin films on copper(I) oxide water splitting photocathodes: a study on performance and stability. Energy & Environmental Science 5, 8673–8681 (2012).
- Klahr, B., Gimenez, S., Fabregat-Santiago, F., Bisquert, J. & Hamann, T. W. Electrochemical and photoelectrochemical investigation of water oxidation with hematite electrodes. Energy & Environmental Science 5, 7626–7636 (2012).
- Klahr, B. M., Martinson, A. B. F. & Hamann, T. W. Photoelectrochemical Investigation of Ultrathin Film Iron Oxide Solar Cells Prepared by Atomic Layer Deposition. Langmuir 27, 461–468 (2011).
- Liu, R. et al. Water Splitting by Tungsten Oxide Prepared by Atomic Layer Deposition and Decorated with an Oxygen-Evolving Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int Ed 50,499–502 (2010).